Embedding risk management into decision making
It’s official. We live in uncertain times.
Just pick up today’s paper and the headlines are screaming with news that constantly remind us that we are living uncertain times – economic instability, pandemic, corporate restructures, etc.
Uncertainty can be uncomfortable, but inevitable
Throughout our lives, the fear of the unknown can keep us from taking the actions to move us forward.
The reality is that in our fast-changing, unpredictable and accelerated workplace and the world, it’s those who are willing to embrace uncertainty and take decisive action, risky action, despite the many unknowns who will reap the greatest rewards.
Human beings are wired to want to control our environment.
Let’s face it, it’s a natural human instinct to strive for familiarity when something feels uncertain or not known.
Your brain is hardwired to protect you from risk and danger. You often discard an idea in favour of something that feels familiar, safer.
But if you continually avoid the ‘what ifs’, it can dramatically affect your capacity to innovate and to grow. Not to mention, it can erode your ability to succeed in today’s fast-moving world.
So, what might be possible if you moved beyond the known zone and embrace uncertainty?
This is no easy feat to overcome. You are human, after all.
But I can offer a practical decision-making framework that can help you make decisions under uncertainty.
Making decisions under uncertainty
Various internet sources estimate that an adult makes up to 35,000 remotely conscious decisions each day – What to eat? What career will I pursue? Where to invest my savings? What marketing strategy to adopt? Who to hire?
Each choice carries certain consequences – good and bad. This ability to choose is an incredible and exciting power that has been entrusted to you by your Creator.
Choices compound. These accumulated choices all work together over a lifetime to take you to various outcomes.
If you are a manager or leader, your decisions will interact with the choices and actions of other people. Your leadership decisions create a ripple effect for spouses, families, teams, business units, organisations, communities, states, nations and even the world-at-large.
Practical approaches to making informed decisions
This is where the PrOACT decision-making framework.
The structured framework contains the following elements:
- Find the right problem to start with.
- Identify your real objectives.
- Create a range of alternatives tailored to your problem and objectives.
- Understand the consequences each alternative would have for each of your objectives.
- Make trade-offs among conflicting objectives.
- Identify opportunities and uncertainties that may affect your decision and objectives.
- Take account of your risk-taking attitude.
- Plan for linked decisions over time.

The reason why I like the PrOACT decision-making framework to start with is that you must explicitly consider opportunities and uncertainties when you are making decisions in uncertain or volatile situations.
As the world becomes more uncertain, I foresee that this framework will gain prominence over time.
Proactively identifying and managing opportunities and uncertainties under uncertainty
The reality is that you are identifying and managing risk, or know opportunities and uncertainties, all the time, at home and at work, consciously or unconsciously.
When you cross a busy road to buy lunch, there are uncertainties lurking around. Drunk drivers. Speeding drivers.
In applying for a new job, you can be uncertain about how your skills will fit into the working environment, your capability to perform in a new role, etc.
You can also be uncertain about the report you are writing for your manager due to the complexity of the subject matter.
The international risk management, ISO 31000, provides further contemporary guidance when applying Element 6 of the PrOACT decision-making framework.
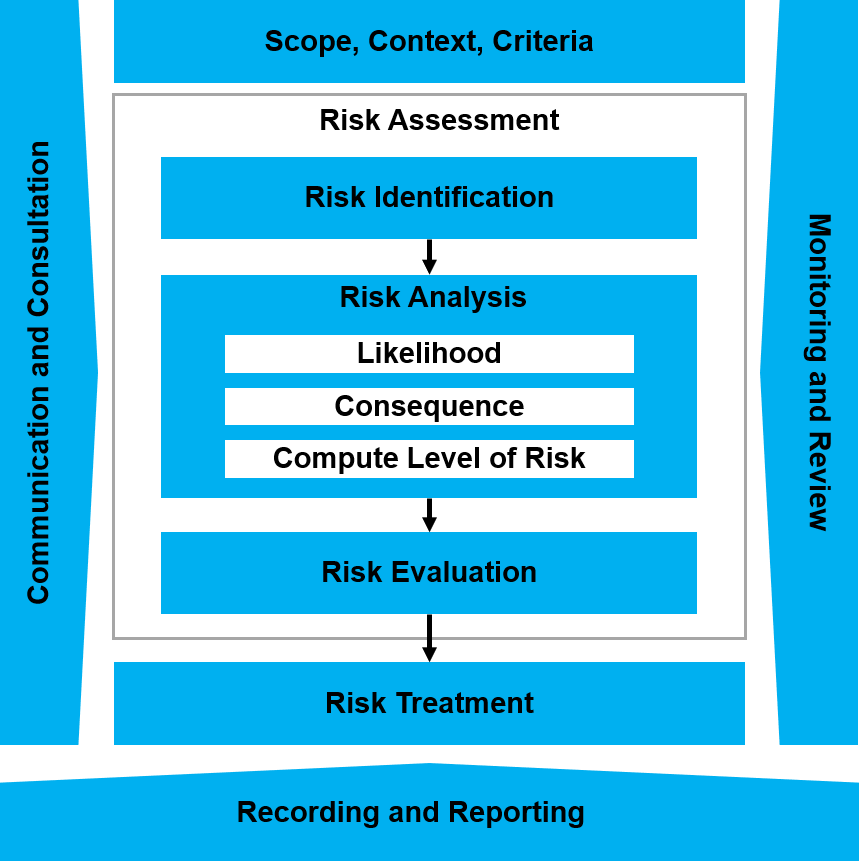
The ISO 31000 risk management process involves a systematic application of policies, procedures and practices to the activities of communicating and consulting, establishing the context and assessing, treating, monitoring, reviewing, recording and reporting risk.
The risk management process comprises the activities described in the diagram shown below.
There are significant overlaps between the PrOACT decision-making framework and the ISO 31000 risk management process.
The ISO 31000 risk management process provides an internationally accepted and structured process for identifying and managing known opportunities and uncertainties. This will increase the likelihood and extent of your success when you make better-informed decisions and solving problems.
What is important to note is that Element 6 of the PrOACT decision-making framework have been expanded and strengthen to incorporate the following ISO 31000 risk management activities:
- Risk assessment, which is the overall process of:
- Risk identification – A process of finding, recognising and describing risks, or known opportunities and uncertainties.
- Risk analysis – A process to comprehend the nature of risk and to determine the level of risk or risk rating.
- Risk evaluation – A process of comparing the results of your risk analysis with risk criteria to determine whether the risk and/or its magnitude is acceptable or tolerable. The risk criteria can be based on your decision criteria, which is usually developed under the PrOACT decision-making framework, Element 2 – Identify your real objectives.
- Risk treatment – An activity to select and implement options for addressing risk or enhancing opportunities. Having completed a risk assessment, treating a risk involves selecting and implementing one or more treatment options that will change the likelihood of occurrence, the consequences of the risk, or both.
All other activities of the ISO 31000 risk management process can be incorporated into other elements of the PrOACT decision-making framework. Hence, the overlap between the two.
PrOACT 31000 – A practical framework for making informed decisions under uncertainty
What makes the PrOACT 31000 decision-making framework powerful is that it has taken the best of the original PrOACT framework and embeds the international best practice in risk management, which is taken from ISO 31000 international risk standard.
This gives a contemporary and wholesome approach to making decisions and solving problems under uncertainty.
The PrOACT 31000 framework for making better-informed decisions under uncertainty contains the following elements:
- Find the right problem to start with.
- Identify your real objectives.
- Create a range of alternatives tailored to your problem and objectives.
- Understand the consequences each alternative would have for each of your objectives.
- Make trade-offs among conflicting objectives.
- Review your problem definition, objectives, alternatives and consequences.
- Identify opportunities and uncertainties that may affect your decision and objectives.
- Take account of your risk-taking attitude.
- Plan for linked decisions over time.

Uncertainty can ultimately enrich your life or diminish it when you have the right approach and tools at hand.
The modified PrOACT 31000 decision-making framework is one such tool that could give you the required confidence to be in control over your decision-making process where informed decisions are made under uncertainty.
The PrOACT 31000 decision-making framework incorporates the elements of the PrOACT framework and key activities of the international risk management standard, ISO 31000.
This powerful combination provides a very practical but systematic approach to making inform decisions. While you cannot control the outcome of your decisions, the structure and framework provide the necessary conditions and foundations for making quality decisions
Embrace it by practising making informed decisions under uncertainty using the PrOACT 31000 framework that incorporates the international risk management process taken from the ISO 31000 risk management standard.
